Battery IP Ratings: Ultimate Guide to Dust & Water Protection【2025】
Battery IP Ratings Complete Guide

1. Definition and Structure of IP Ratings
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating, defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC 60529 Standard), classifies the effectiveness of electrical enclosures against solid particles (e.g., dust) and liquids (e.g., water).
- First Digit: Dust protection level (0–6). Higher numbers indicate stronger protection. Examples:
- 6: Dust-tight (no ingress of dust).
- Second Digit: Water resistance level (0–9). Higher numbers indicate better water protection. Examples:
- 7: Protected against immersion in 1 meter of water for 30 minutes.
- 8: Protected against prolonged or deeper immersion (conditions specified by the manufacturer).
2. Common Battery IP Ratings and Applications
Different scenarios demand varying IP ratings:
- IP20/IP22
- Use Case: Indoor energy storage systems (e.g., residential solar batteries). Basic dust and drip protection.
- IP54/IP65
- Use Case: Outdoor equipment (e.g., forklifts, golf carts). Partial dust resistance (level 5) and protection against splashing (level 4) or low-pressure water jets (level 5).
- IP67/IP68
- IP67: Widely used in electric vehicle batteries (e.g., Hycan Z03). Survives 30-minute submersion in 1 meter of water, suitable for heavy rain or short-term flooding.
- IP68: Designed for marine or extreme environments, requiring long-term waterproof sealing.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Systems
- Typically require IP67 to block dust and moisture from damaging the fuel cell stack.
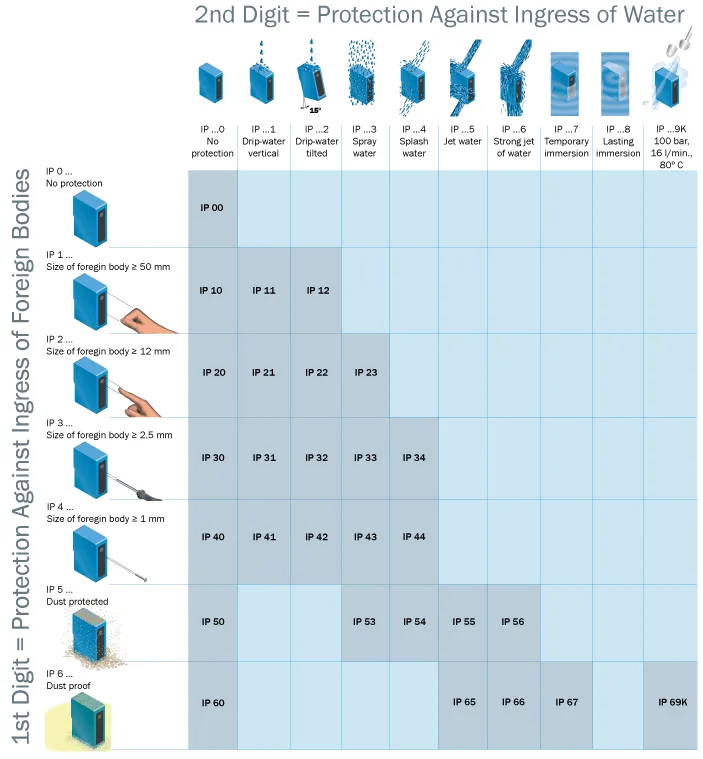
3. Testing Standards and Certification
- Testing Methods
- Dust Testing: Simulated using sand/dust chambers (e.g., GB/T 2423.37).
- Water Testing: Spray nozzles, immersion tanks, etc. (e.g., GB/T 4208-2017).
- Certification
- Compliance with CE, UL, or regional regulations is mandatory for market access.
4. Key Considerations and Usage Tips
Even high IP-rated batteries require caution:
- Avoid Extreme Conditions
- IP67 batteries resist short-term immersion but may fail if submerged long-term (e.g., corroded connectors).
- Water Exposure Strategies
- For EVs, drive slowly through flooded areas to prevent water surges damaging the battery pack.
- Post-Water Damage Actions
- Immediately power off and seek professional inspection if submerged to avoid short circuits or fires.
- Maintenance
- Regularly check seals, housing integrity, and aging components to maintain IP performance.

5. Summary
Selecting the right IP rating is critical for battery safety and longevity:
- Indoor/Low-Risk: IP20–IP54.
- Outdoor/High Humidity: IP65 or higher.
- Extreme Environments (Marine, Flooding): Prioritize IP67/IP68.
For detailed testing protocols or certifications, refer to IEC 60529 or GB/T 4208.
This guide balances technical accuracy with readability, making it suitable for engineers, buyers, and end-users. Let me know if you need further customization!






One Comment