Battery Energy Storage Systems: Your Simple Guide
Have you ever wondered how we can save extra energy to use later, just like saving money in a bank? That’s exactly what a battery energy storage system does! Let’s break down what it is, how it works, and answer some common questions.
What is an Energy Storage Battery?
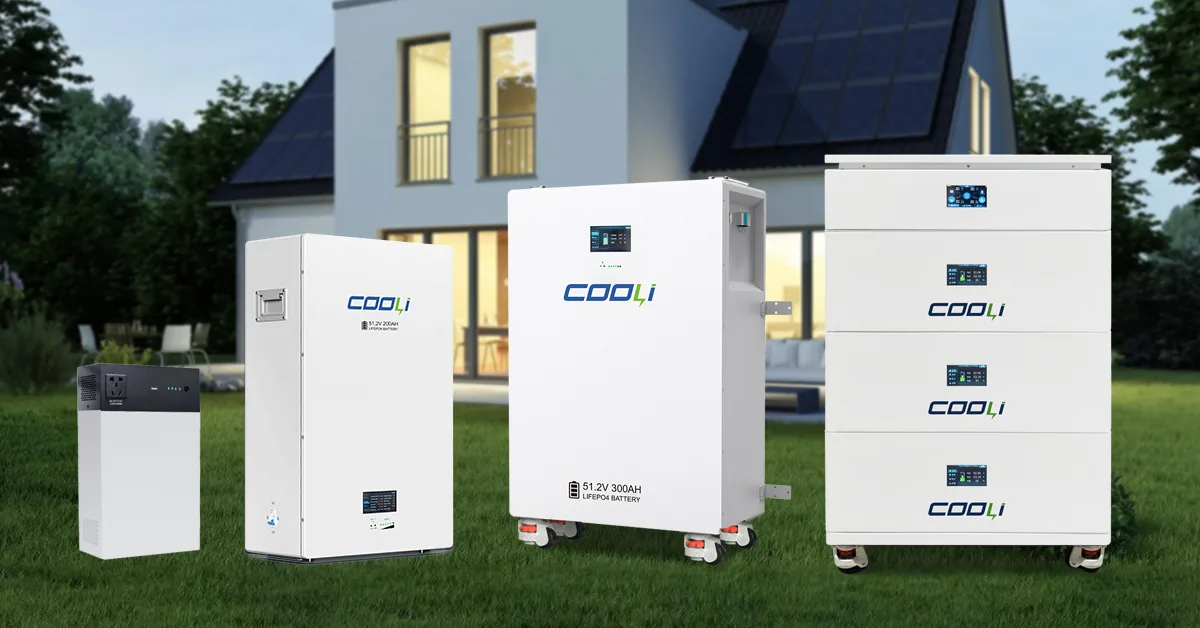
An energy storage battery is like a giant, powerful version of the battery in your phone or laptop. Its main job is to store electrical energy so that it can be used at a different time. Think of it as a “power bank” for your home, business, or even the entire electrical grid.
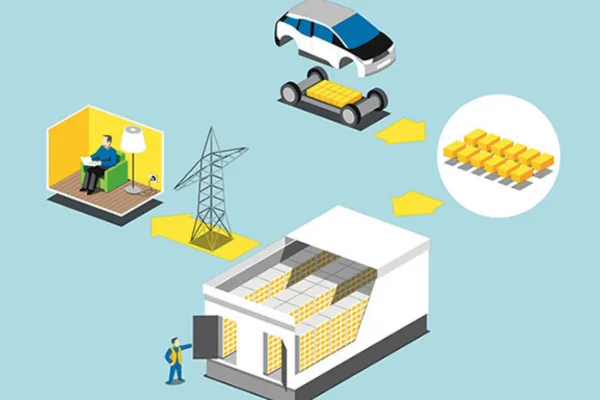
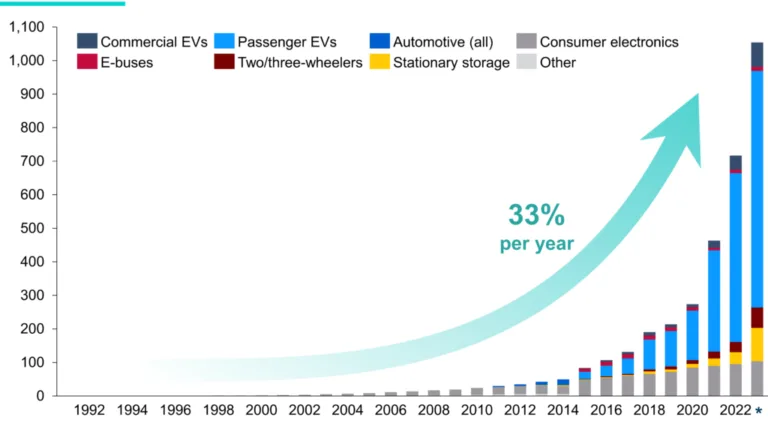
These systems are crucial for using more renewable energy. For example, solar panels make electricity when the sun is shining, and wind turbines spin when the wind is blowing. But what happens at night or on a calm day? The energy storage battery saves the extra power generated during sunny or windy times and releases it when needed.
How Does a Battery Energy Storage System Work?
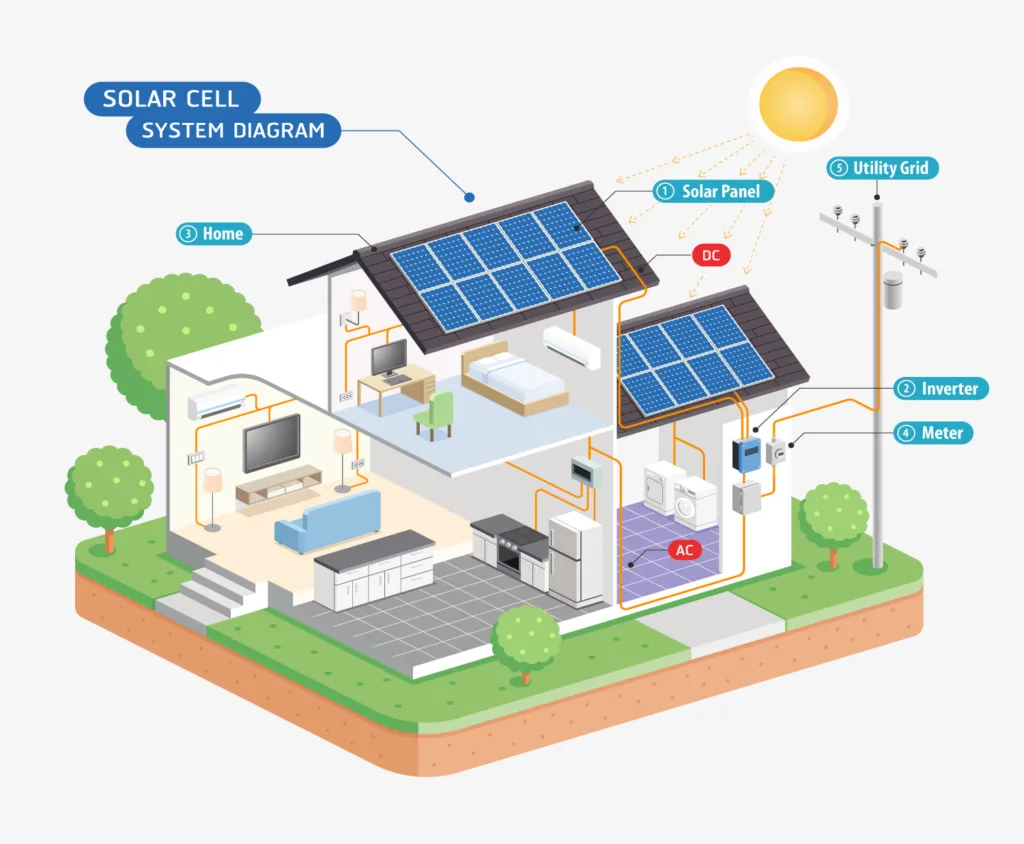
A battery energy storage system has three main parts:
- The Battery: This is where the energy is stored chemically. Most large systems today use lithium-ion batteries (similar to electric car batteries) because they are efficient and can store a lot of energy.
- The Inverter/Converter: This is the “brain” of the system. Electricity can be in two forms: AC (Alternating Current), which is what our homes use, and DC (Direct Current), which is what batteries store. The inverter converts DC electricity from the batteries to AC for your home. It also converts AC electricity from the grid or solar panels to DC to charge the batteries.
- The Control System: This smart software manages everything. It decides when to charge the batteries (like when energy is cheap or there’s extra solar power) and when to discharge them (like during a power outage or when energy prices are high).
In simple terms: Charging (AC to DC) → Storing (energy sits in the battery) → Discharging (DC to AC).

Are Battery Energy Storage Systems Safe?
This is a very important question. The short answer is yes, when they are properly designed, installed, and maintained.
Like any technology that stores energy, there are potential risks, such as overheating or fire. However, modern systems are built with many layers of safety:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): This is like a guardian for the battery. It constantly monitors temperature, voltage, and current to prevent overcharging or overheating.
- Thermal Management: Systems have cooling (or sometimes heating) systems to keep the batteries at their ideal temperature.
- Safety Enclosures: Batteries are often housed in fire-resistant containers and installed in secure, well-ventilated areas.
- Codes and Standards: Professional installations follow strict electrical codes and safety standards to ensure they are safe.
While no system is 100% risk-free, reputable manufacturers prioritize safety, making these systems very safe for homes and businesses.

How to Size a Battery Energy Storage System
“Sizing” means choosing a system that is the right size for your needs. It’s like deciding whether you need a small water bottle or a large jug for a hike. You don’t want one that’s too small (you’ll run out of power) or too large (you’ve wasted money).
Here’s what you need to consider:
- Your Goal: Why do you want a battery?
- Backup Power: To keep your lights and fridge on during a short blackout? You might need a smaller system.
- Energy Independence: To power your entire house all night from solar? You’ll need a much larger system.
- Your Energy Usage: Look at your electricity bill to see how many kilowatt-hours (kWh) you use each day, especially during the times you want to use the battery.
- Power Needs (Load): Make a list of the most important appliances you want to run during an outage (e.g., refrigerator, lights, well pump) and add up their wattage. This tells you how much power (kW) you need at any given moment.
- Duration: How long do you want to power those appliances? This tells you how much energy storage (kWh) you need.
For example, if you need to power appliances that use a total of 2 kW for 5 hours, you would need a battery with at least 10 kWh of capacity.

Because this can get complicated, it’s always best to consult with a professional installer. They can analyze your energy usage and goals to recommend the perfect system size for you.
I hope this guide helps you understand the basics of battery energy storage systems! They are a key technology for building a cleaner, more reliable energy future.