8 Exciting Facts About Lithium Ion Batteries That Will Surprise You
Lithium-ion Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Lithium ion batteries power our everyday lives, from smartphones to electric vehicles. But how much do you really know about them? Understanding their safety, charging methods, recycling options, and travel regulations is essential for responsible use. In this article, we’ll explore 8 key facts about lithium-ion batteries, helping you maximize their lifespan, ensure safety, and dispose of them properly. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just want to handle batteries more safely, this guide has you covered!

1. What is a Lithium-ion Battery?
A Lithium-ion Battery (Li-ion) is a rechargeable battery that stores and releases electrical energy by moving lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes. Since Sony first commercialized it in 1991, it has become a core power source for modern electronics and clean energy systems.
Core Advantages
- High energy density: Stores more energy per unit volume/weight than traditional batteries.
- Long cycle life: Can be charged and discharged 500-1500 times.
- Low self-discharge rate: Loses only 1-2% of charge per month.
- No memory effect: Can be charged at any time without full discharge.
2. What is in a Lithium-ion Battery?
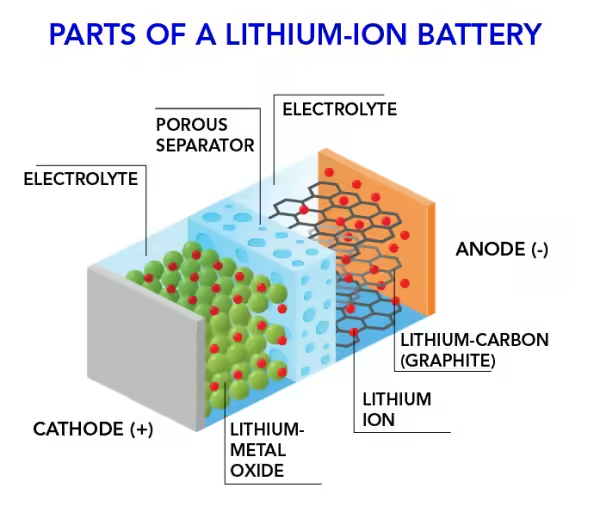
Positive Electrode (Cathode)
Material: Lithium metal oxides such as LiCoO₂, NCM/NCA, or LiFePO₄.
Function: Provides lithium-ion sources and determines battery voltage and capacity.
Negative Electrode (Anode)
Material: Graphite (or silicon-based materials in high-end batteries).
Function: Stores lithium ions and releases/receives electrons.
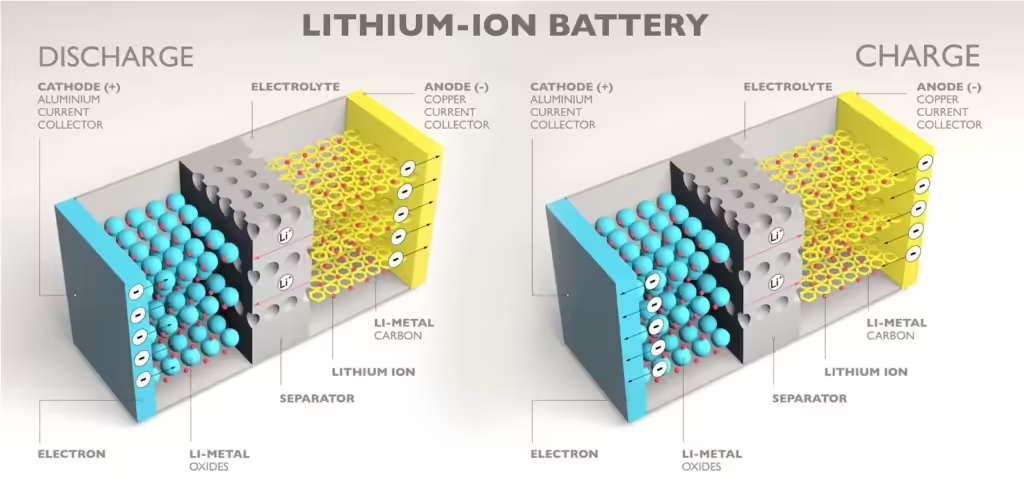
3. How do lithium ion batteries work?
Lithium-ion batteries work by shuttling lithium ions between electrodes:
- Charging: Lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode.
- Discharging: Lithium ions return to the cathode, generating power.
Check out the dedicated explanation: https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/articles/how-lithium-ion-batteries-work
4. How to charge lithium ion battery?
- Avoid extreme charge levels (20%-80% recommended).
- Charge at optimal temperatures (10°C to 30°C).
- Use original chargers for safety.
5. Are lithium ion batteries safe?
Thermal runaway can occur due to:
- Mechanical abuse (puncturing causing short circuits).
- Electrical abuse (overcharging, over-discharging).
- Thermal abuse (high-temperature exposure).
6. Can you take lithium ion batteries on airplanes?
According to ICAO regulations:
- Checked baggage: Prohibited due to fire risks.
- Capacity limits:
- <100Wh: No declaration required.
- 100Wh-160Wh: Requires airline approval.
- >160Wh: Prohibited.
7. Can lithium ion batteries be recycled?
Why recycle? Recycling lithium, cobalt, and nickel is important for several reasons:
- Limited Resources: Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are finite resources, and with the growing demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage, extraction becomes more difficult and costly.
- Environmental Impact: Mining these materials can harm the environment, polluting water, land, and ecosystems. Recycling helps reduce these environmental burdens.
- Economic Benefits: Recycling these materials is cheaper than mining new ones and can create jobs in the recycling industry.
- Sustainability: Recycling creates a circular economy, reducing waste and ensuring resources are available for future generations.
- Technological Advances: With improved recycling technologies, the process becomes more efficient, allowing for better extraction of these valuable metals.
Recycling Methods
- Pyrometallurgy: High-temperature metal extraction.
- Hydrometallurgy: Chemical dissolution for metal separation.
- Direct regeneration: Restores cathode materials for reuse.
8. Future Battery Technologies
- Solid-state batteries: Higher safety and energy density.
- Sodium-ion batteries: Cost-effective for large-scale energy storage.
- Lithium-sulfur batteries: Higher energy density, but durability remains a challenge.

