What is an Energy Storage Battery? A Beginner’s Guide【2025】
Demystifying Energy Storage Batteries: Your Essential Guide
Ever wondered how we can capture sunshine during the day to power our homes at night? Or how electric vehicles drive hundreds of miles on a single charge? The unsung hero enabling these modern marvels is the energy storage battery.
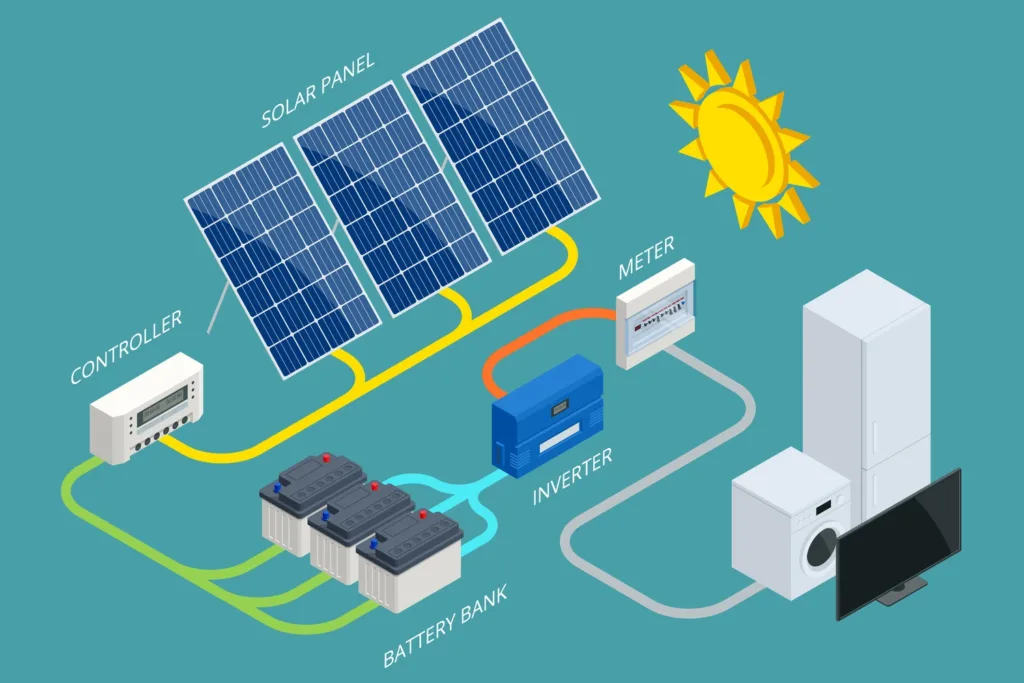
In simple terms, an energy storage battery is a device that stores electrical energy chemically and releases it as electricity when needed. Think of it like a rechargeable water tank for electricity: you fill it up (charge it) when water (electricity) is plentiful or cheap, and you draw from it (discharge it) when you need water (power) but the tap isn’t flowing sufficiently.
Why Do We Need Energy Storage Batteries?
Our traditional power grids are built for immediate use – electricity is generated (at power plants) and consumed (in our homes and businesses) almost instantly. This creates challenges:
- Intermittent Renewables: Solar panels only produce power when the sun shines, and wind turbines only spin when the wind blows. Batteries store excess renewable energy for use when generation is low.
- Peak Demand: Electricity usage spikes during certain times (e.g., hot evenings). Power plants struggle to meet this peak demand efficiently, often relying on expensive or polluting “peaker” plants. Batteries can discharge during peaks, reducing strain and cost.
- Grid Stability: Batteries can respond incredibly fast (milliseconds) to fluctuations in supply or demand, helping maintain the grid’s stable frequency and voltage.
- Backup Power: Provide crucial electricity during grid outages (like storms), keeping lights on, refrigerators running, and medical devices operating.
- Energy Independence: Paired with rooftop solar, batteries allow homes and businesses to use more of their own clean energy, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering bills.

How Do Energy Storage Batteries Work? (The Simple Version)
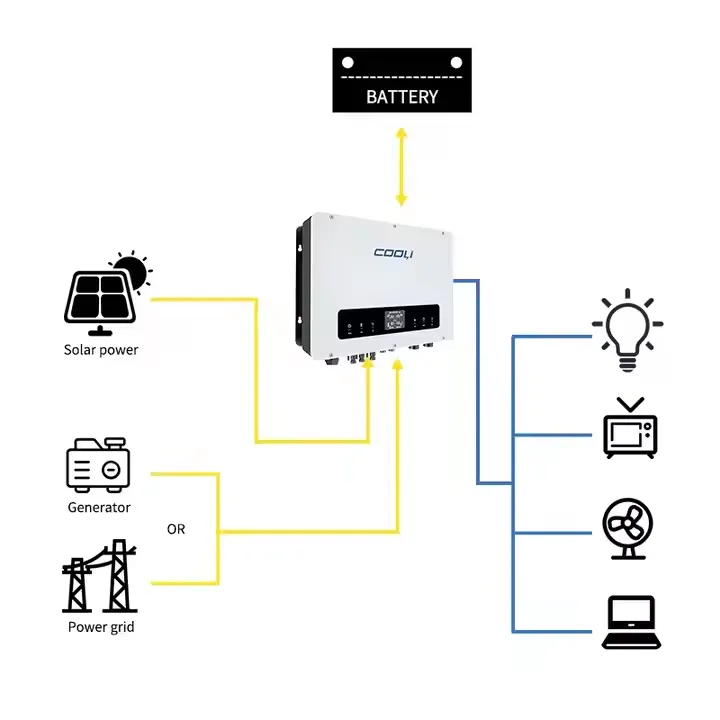
- Charging: When connected to an electricity source (like solar panels or the grid), an electric current flows into the battery. This current drives chemical reactions inside the battery, storing energy in the form of chemical potential energy.
- Storing: The energy remains stored chemically until it’s needed.
- Discharging: When you need power (e.g., at night or during an outage), the chemical reactions reverse. Electrons flow out of the battery as an electric current, powering your devices.
- The Inverter: Batteries store and release Direct Current (DC) electricity. Our homes and the grid use Alternating Current (AC). A crucial component called an inverter converts the battery’s DC electricity into usable AC electricity for your appliances.
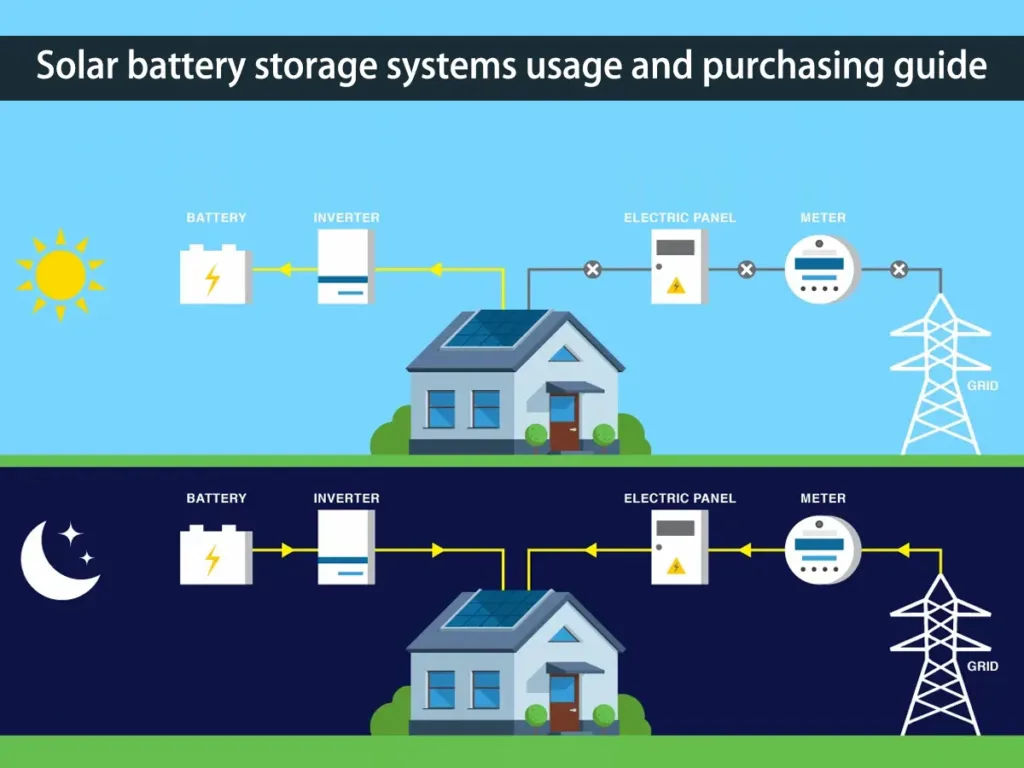
Common Types of Energy Storage Batteries:
While many technologies exist, these dominate the market for home, business, and grid-scale storage:
- Lithium-Ion (Li-ion): The most common type today (similar to your phone/laptop battery, but larger and more robust). Examples include Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC).
- Pros: High energy density (lots of storage in a small space), high efficiency, long lifespan, relatively fast charging/discharging.
- Cons: Higher upfront cost (though decreasing), thermal management needs (can overheat), concerns about raw material sourcing.
- Lead-Acid: The older, mature technology (like car batteries). Still used for some backup applications.
- Pros: Lower upfront cost, well-understood technology, recyclable.
- Cons: Lower energy density (bulkier/heavier), shorter lifespan, slower charging, lower efficiency, requires ventilation.
- Flow Batteries: (Emerging for large-scale storage) Store energy in liquid electrolytes held in external tanks.
- Pros: Very long lifespan, easy to scale capacity (bigger tanks), potentially safer.
- Cons: Lower energy density (large footprint), complex systems, higher cost, less mature for smaller applications.
LiFePO4 Battery vs. Lithium-Ion: A Comprehensive Guide
Lithium vs Lead-Acid Battery: Comprehensive Comparison & Buying Guide【2025】
Key Terms You Might Hear:
- Capacity (kWh): How much total electricity the battery can store (like the size of your fuel tank). A 10 kWh battery could theoretically power a 1 kW appliance for 10 hours.
- Power Rating (kW): How much electricity the battery can deliver at one time (like the size of the fuel line). A 5 kW battery can run multiple appliances simultaneously, up to 5,000 watts.
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): The percentage of the battery’s capacity that can be safely used (e.g., 90% DoD means you shouldn’t use the last 10% to preserve lifespan).
- Round-Trip Efficiency: The percentage of energy put into the battery that you can usefully get out (e.g., 90% efficiency means you lose 10% during the charge/discharge cycle).
- Cycle Life: The number of complete charge/discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly degrades.
Where You’ll Find Them:
- Residential: Tesla Powerwall, LG Chem RESU, Enphase IQ Battery etc. – paired with solar panels or for backup.
- Commercial/Industrial: Larger systems to reduce peak demand charges, provide backup, or integrate renewables.
- Utility-Scale: Massive battery installations (often using shipping containers full of battery racks) directly connected to the grid to provide stability, store renewable energy, and defer grid upgrades.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): The battery pack is the energy storage system powering the car.
The Future is Bright (and Stored!)
Energy storage batteries are no longer science fiction; they are essential technology rapidly transforming our energy landscape. As costs continue to fall, efficiency rises, and new chemistries emerge (like solid-state), batteries will play an even bigger role in enabling a cleaner, more resilient, and more efficient energy future powered by renewables.
Getting Started:
If you’re curious about batteries for your home, start by researching reputable brands, understanding your energy usage patterns, and consulting with qualified solar+storage installers. For the grid and large-scale applications, ongoing advancements promise even greater capabilities and integration.
Energy storage batteries are the key to unlocking the full potential of renewable energy and building a more sustainable and reliable power system for everyone. It’s an exciting technology worth understanding!







2 Comments