Battery Capacity and Power Calculation: Complete Practical Guide for Solar & Energy Storage Systems
Understanding battery capacity and power calculation is essential when designing a solar energy storage system, backup power solution, or off-grid installation. Choosing the wrong battery size can lead to power shortages, wasted investment, or system instability.
This guide explains battery capacity, power ratings, formulas, real examples, and system sizing methods in simple terms.
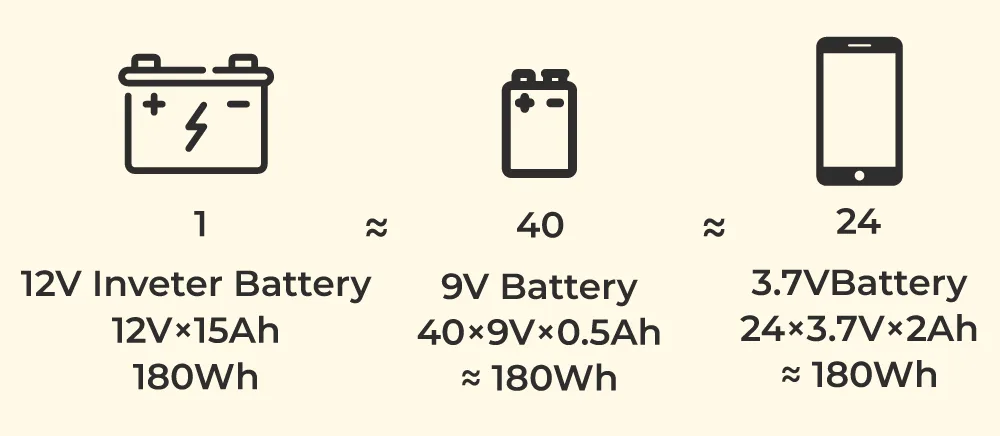
What Is Battery Capacity?
Battery capacity shows how much energy a battery can store and deliver over time. It is usually measured in:
- Amp-hours (Ah) — current × time
- Watt-hours (Wh) — energy capacity
- Kilowatt-hours (kWh) — large system storage capacity
Basic Formula
Battery Capacity (Wh) = Voltage (V) × Amp-hours (Ah)
Example:
- 12V 100Ah battery
- Capacity = 12 × 100 = 1,200 Wh = 1.2 kWh
This is the most important foundation of battery capacity and power calculation.

What Is Battery Power?
Battery power refers to how fast energy can be delivered at a given moment. It is measured in:
- Watts (W)
- Kilowatts (kW)
Power determines:
- How many devices can run simultaneously
- Whether heavy loads (motors, pumps, air conditioners) can start
- Peak discharge capability
Capacity vs Power — Key Difference
| Item | Capacity | Power |
|---|---|---|
| Energy stored | How much | — |
| Delivery speed | — | How fast |
| Unit | Wh / kWh | W / kW |
| Example | 10 kWh battery | 5 kW output |
A battery may store a lot of energy but still be unable to deliver high power if its discharge rating is low.
Core Battery Capacity and Power Calculation Formulas
1️⃣ Energy Calculation
Energy (Wh) = Power (W) × Time (hours)
Example:
- Load = 300W
- Runtime = 5 hours
Energy needed = 300 × 5 = 1,500 Wh
2️⃣ Required Battery Capacity
Required Capacity (Ah) = Energy (Wh) ÷ Voltage (V)
Example:
- Required energy = 1,500 Wh
- System voltage = 24V
Capacity = 1,500 ÷ 24 = 62.5 Ah
3️⃣ Include Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Not all stored energy is usable.
- Lead acid DoD ≈ 50%
- LiFePO4 DoD ≈ 80–95%
Adjusted Capacity = Required Capacity ÷ DoD
Example with LiFePO4 (90% DoD):
62.5 ÷ 0.9 = 69 Ah
4️⃣ Add Safety Margin
Add 10–20% for losses and aging:
Final size ≈ 80 Ah

Solar Battery Capacity Calculation Example
Scenario: Home Backup System
Devices:
- Lights = 200W
- Refrigerator = 150W
- TV + Router = 150W
Total load = 500W
Required runtime = 6 hours
Energy needed:
500 × 6 = 3,000 Wh = 3 kWh
Using a 48V LiFePO4 battery:
3,000 ÷ 48 = 62.5 Ah
Adjust for 90% DoD:
62.5 ÷ 0.9 ≈ 70 Ah
Recommended battery: 48V 100Ah LiFePO4
Battery Power Calculation for Load Support
Besides capacity, check discharge power.
Formula:
Max Power = Battery Voltage × Max Discharge Current
Example:
- Battery = 48V
- Max discharge = 100A
Power = 48 × 100 = 4,800W (4.8kW)
Your inverter load must stay within this limit.
Peak vs Continuous Power
Important for battery capacity and power calculation:
- Continuous power = steady output
- Peak power = short burst (motor startup)
Motor loads may require 3–5× startup power.
Always check:
- Battery BMS peak rating
- Inverter surge rating

LiFePO4 vs Lead Acid in Capacity Calculations
| Factor | LiFePO4 | Lead Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Usable capacity | 90% | 50% |
| Cycle life | 4000–6000 | 300–500 |
| Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
This means LiFePO4 systems require smaller nominal capacity for the same usable energy.
Modern suppliers such as COOLI (coolienergy.com) provide LiFePO4 batteries with high usable capacity, integrated BMS, and scalable storage for solar projects and OEM systems.
System Voltage and Capacity Planning
Higher voltage systems reduce current and cable loss.
| System | Best Use |
|---|---|
| 12V | Small setups |
| 24V | Medium systems |
| 48V | Home & commercial storage |
For larger solar storage systems, 48V or higher improves efficiency and safety margins.

Quick Sizing Rule of Thumb
You can estimate battery capacity using:
Daily Energy Use (kWh) × Backup Days ÷ DoD
Example:
- Daily use = 5 kWh
- Backup = 1 day
- DoD = 90%
5 ÷ 0.9 = 5.6 kWh battery
Featured Snippet Optimized Answer
Battery capacity is calculated by multiplying battery voltage by amp-hour rating (Wh = V × Ah). Battery power is calculated by multiplying voltage by discharge current (W = V × A). Capacity shows stored energy, while power shows delivery speed.
FAQ – Battery Capacity and Power Calculation
How do I calculate battery capacity for my home?
Multiply your total load (W) by runtime (hours) to get Wh, then divide by battery voltage and adjust for DoD.
Is kWh more important than Ah?
For system planning, kWh is more useful because it reflects real energy storage.
Can a high-capacity battery deliver high power?
Not always. You must check maximum discharge current and BMS limits.
Why is LiFePO4 better for energy storage calculation?
Because it allows deeper discharge, higher efficiency, and longer cycle life — reducing required nominal capacity.





![[Guia 2025]Bateria Solar no Brasil: 72% de Economia + Luz 24h! 🔋 此图片的 alt 属性为空;文件名为 image-31-png.webp](https://coolithium.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/image-32.webp)

One Comment